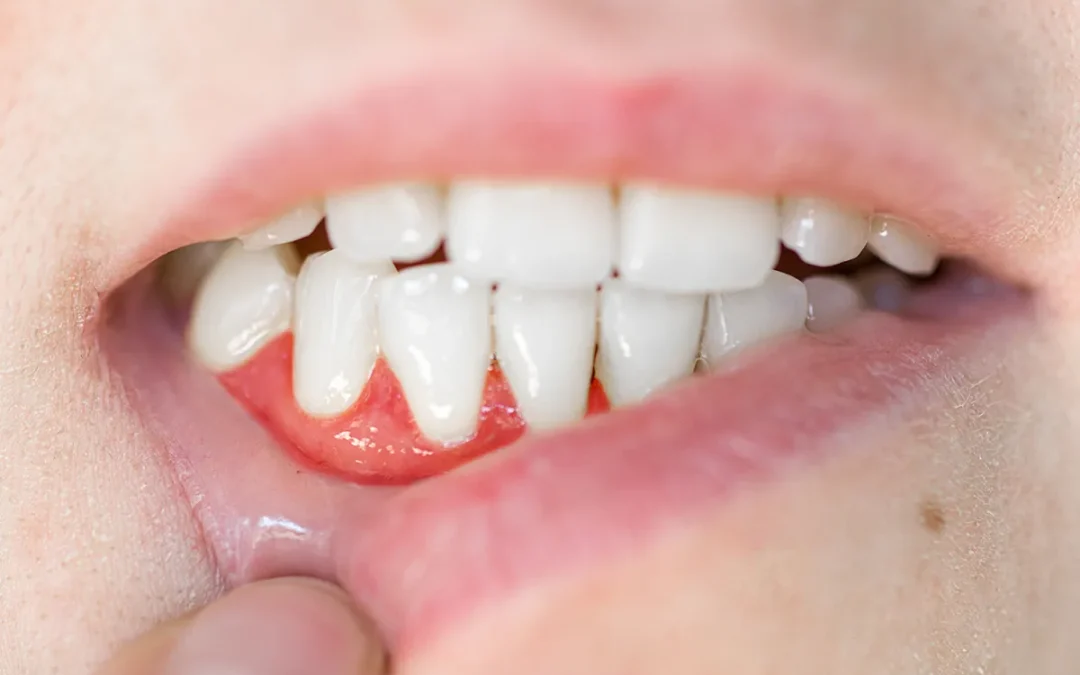
Gum disease: Causes, symptoms, prevention & treatment
Gum disease — often underestimated yet surprisingly widespread — affects 1 in 5 children and nearly 1 in 3 adults in Australia. Also known as periodontal disease, this condition doesn’t just impact your gums; it can have far-reaching effects on your overall well-being. The good news? With the right knowledge and care, gum disease is largely preventable.
Let’s explore what gum disease is, its root causes, early warning signs, and the most effective ways to prevent and treat it. By understanding gum disease, you’ll be empowered to take proactive steps toward maintaining a healthy smile and safeguarding your health.
What is gum disease?
Gum disease is an infection that affects the gums and the supporting structures around your teeth. It typically develops in stages, with each stage presenting different levels of severity:
- Gingivitis: This is the earliest and mildest form of gum disease. It causes symptoms like gum irritation, redness, and swelling. The good news is that gingivitis is reversible with consistent brushing, flossing, and professional dental care.
- Periodontitis: When gingivitis is left untreated, it can advance to periodontitis. This more serious stage leads to damage of the bone and tissues that hold your teeth in place. Over time, this can cause gums to recede, teeth to loosen, and, in severe cases, tooth loss. Effective treatment is crucial to stop further damage and preserve your oral health.
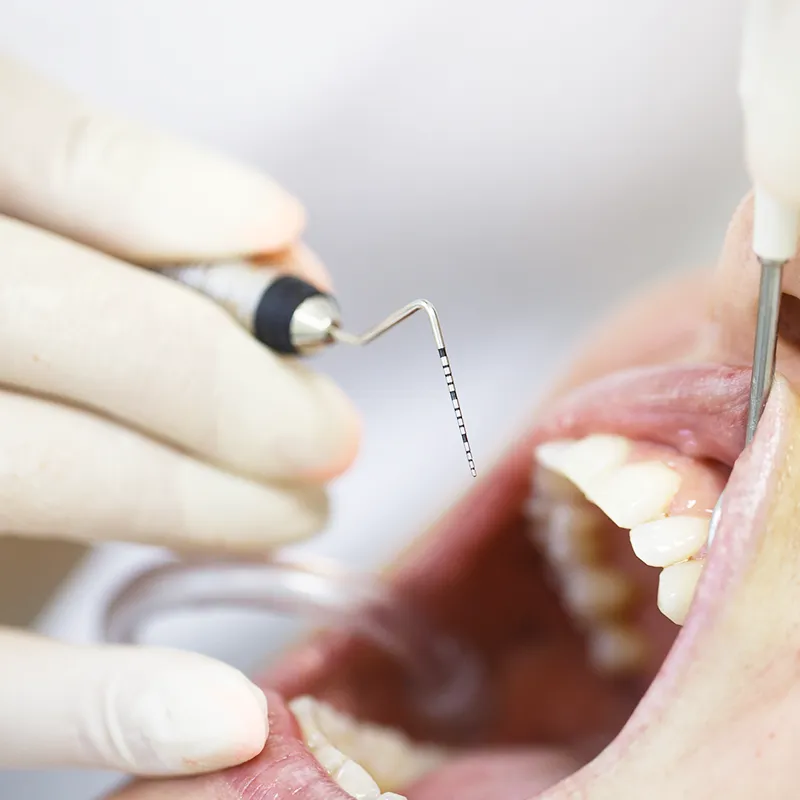
Causes of gum disease
Gum disease is primarily caused by the buildup of plaque — a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth. If plaque is not removed by brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar (calculus), which can only be removed by a dentist or dental hygienist. The following factors can contribute to the development of gum disease:
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing allow plaque to accumulate.
- Smoking: Smoking cigarettes is a significant risk factor for gum disease and can impair healing.
- Genetics: Some people may be genetically predisposed to gum disease.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes and autoimmune diseases can increase susceptibility.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause can make gums more sensitive.
- Medications: Certain medications reduce saliva flow, increasing plaque buildup.
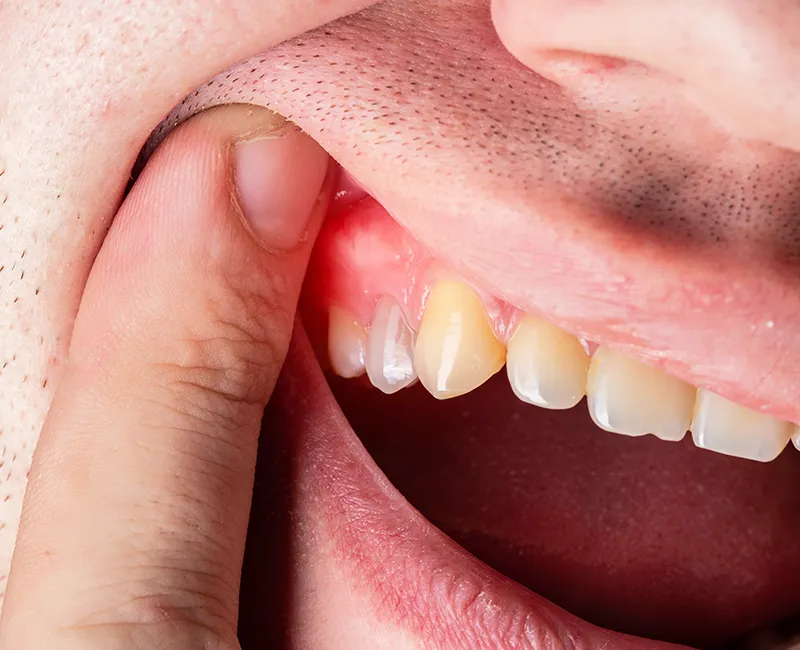
Symptoms of gum disease
Gum disease can often go unnoticed in its early stages, which is why regular dental checkups are essential. Common symptoms include:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding gums, especially when brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Receding gums or teeth appear longer
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Painful chewing
- Formation of deep pockets between teeth and gums

How to prevent gum disease
Preventing gum disease is far simpler than treating it. Incorporate these key habits into your daily routine to maintain healthy gums:
- Brush twice a day: Use fluoride toothpaste and brush for at least two minutes, paying extra attention to the gum line where plaque tends to build up.
- Floss daily: Flossing helps remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gum line, where your toothbrush may not reach
- Schedule regular dental checkups: Visit your dentist every six months for professional cleanings and examinations to detect and address early signs of gum disease.
- Quit smoking: If you smoke, quitting can drastically improve your gum health and reduce your risk of gum disease.
- Eat a balanced diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, supports healthy gums and teeth.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash: Rinsing with an antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce plaque buildup, control bacteria, and minimise gum inflammation.
Treatment options for gum disease
If you’re diagnosed with gum disease, several treatment options are available depending on the severity of your condition:
1. Professional cleaning (Prophylaxis): For mild gingivitis, routine dental cleaning can effectively remove plaque and tartar buildup, giving your gums a chance to heal.
2. Scaling and root planing: This deep-cleaning procedure targets plaque and tartar below the gum line. The dentist or hygienist also smooths the tooth roots to encourage the gums to reattach and reduce the risk of further infection.
3. Medications: Antibiotics, antimicrobial mouth rinses, or prescription gels may be recommended to control and reduce bacterial infection.
4. Surgical treatments: In advanced cases of periodontitis, surgical interventions may be necessary. Options include:
a. Flap surgery (Pocket reduction surgery): The gums are lifted back to remove deep tartar deposits, and the gum tissue is sutured back in place for better fit.
b. Gum grafts: Tissue from another part of your mouth is used to cover exposed roots and reinforce receding gums.
Prompt treatment is essential to stop the progression of gum disease and prevent serious complications. Your dentist will recommend the best approach based on your specific needs.
Complications of untreated gum disease
Ignoring gum disease can lead to serious complications that extend beyond your oral health, including:
Tooth loss: Advanced periodontitis can destroy the bone and tissues that support your teeth, leading to loose teeth or tooth loss.
Systemic health issues: Research has linked gum disease to an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, diabetes, respiratory infections, Alzheimer’s disease, and pregnancy complications such as premature birth or low birth weight.
Gum and jaw abscesses: Untreated gum infections can result in painful abscesses—pockets of pus—in the gums or jawbone, which may require urgent treatment.
Addressing gum disease early helps prevent these serious health problems and safeguards your oral and overall health.
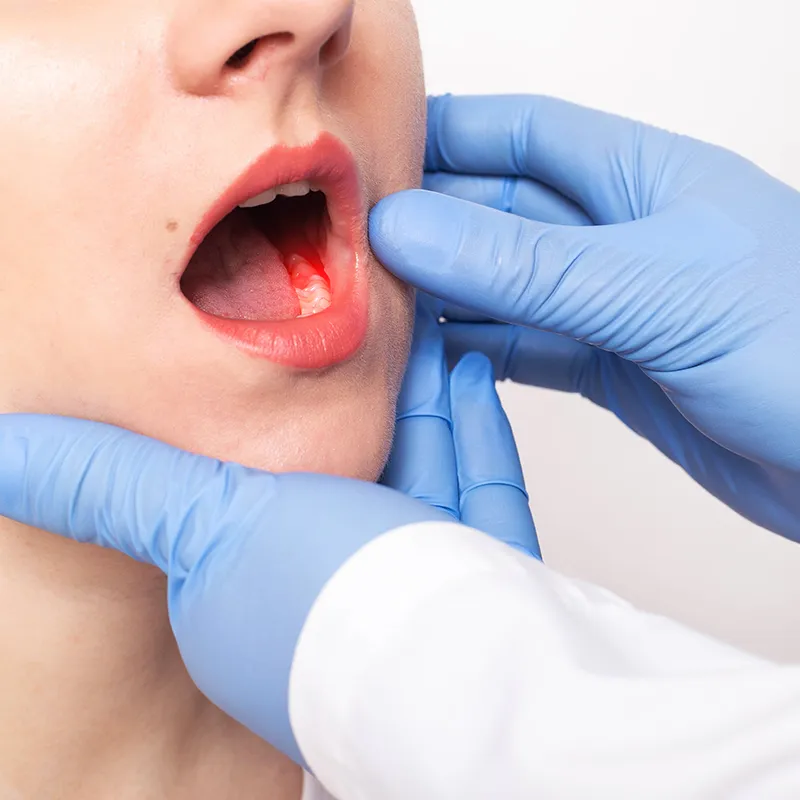
Take care of your gums for a healthier smile and body
Gum disease doesn’t have to stop you from enjoying a healthy, confident smile. By practising good oral hygiene, recognising the early signs of gum issues, and maintaining regular dental checkups, you can protect your gums and enhance your overall health. Prevention and early intervention are your strongest shield, so if you notice any concerns, don’t hesitate to consult your dentist.
Your smile is worth the effort! If you found this blog helpful, explore our other articles for more tips and insights on maintaining optimal oral health.

About the author
Dr. Yulian Wei is a highly skilled dentist with extensive experience in a range of dental practices across Brisbane. Known for her compassionate and effective care, she specialises in supporting patients with dental anxiety. Dr. Yulian’s gentle approach and patient-focused philosophy have helped countless individuals overcome their fears and achieve excellent oral health.
Learn more about Dr. Yulian and his practice: Everyday Smiles Dental Practice